js树结构操作
AprilTong 10/8/2021 Javascript
# js 树结构遍历
树结构介绍
js 中树结构一般是类似于这样的结构
// 每个节点的children属性(如果有)是一颗子树,如果没有children属性或者children长度为0,则表示该节点为叶子节点
let tree = [
{
id: '1',
title: '节点1',
children: [
{
id: '1-1',
title: '节点1-1',
},
{
id: '1-2',
title: '节点1-2',
},
],
},
{
id: '2',
title: '节点2',
children: [
{
id: '2-1',
title: '节点2-1',
},
],
},
]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
树的遍历方法
树结构的常用场景之一就是遍历,而遍历又分为广度优先遍历、深度优先遍历,深度优先遍历又分为先序遍历、后序遍历。
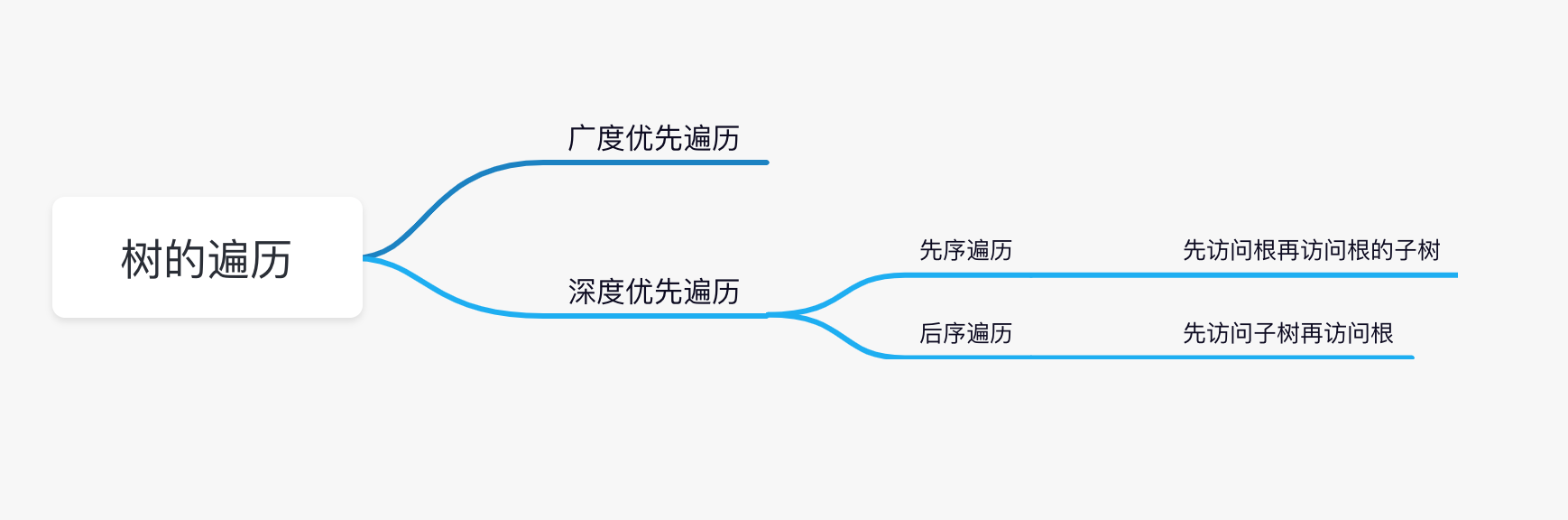
- 广度优先遍历
function treeForeach(tree, fn) {
let node = null
let list = [...tree]
while ((node = list.shift())) {
fn(node)
node.children && list.push(...node.children)
}
}
// 使用
treeForeach(tree, (node) => {
console.log(node.title)
})
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
输出是
// 节点1
// 节点2
// 节点1-1
// 节点1-2
// 节点2-1
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
- 深度优先遍历
- 先序遍历
function treeDeepFoeach(tree, fn) {
tree.forEach((item) => {
fn(item)
// 遍历子树
item.chidren && treeDeepFoeach(item.children, fn)
})
}
// 使用
treeDeepFoeach(tree, (node) => {
console.log(node.title)
})
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
输出
// 节点1
// 节点1-1
// 节点1-2
// 节点2
// 节点2-1
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
后序遍历
与先序遍历思想一致,代码也及其相似,不同的是节点遍历和子树遍历的顺序不一样
function treeDeepFoeach(tree, fn) {
tree.forEach((item) => {
// 遍历子树
item.chidren && treeDeepFoeach(item.children, fn)
fn(item)
})
}
// 使用
treeDeepFoeach(tree, (node) => {
console.log(node.title)
})
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
输出
// 节点1-1
// 节点1-2
// 节点1
// 节点2-1
// 节点2
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
# 列表和树结构相互转换
- 列表转成树
列表结构通常是在节点信息中给定了父级元素的 id,然后通过这个依赖关系将列表转换为树形结构。如下代码:
let list = [
{
id: '1',
title: '节点 1',
parentId: '',
},
{
id: '1-1',
title: '节点 1-1',
parentId: '1',
},
{
id: '1-2',
title: '节点 1-2',
parentId: '1',
},
{
id: '2',
title: '节点 2',
parentId: '',
},
{
id: '2-1',
title: '节点 2-1',
parentId: '2',
},
]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
列表结构转为树结构实现: 把所有非根节点放到对应父节点的 children 数组中,然后把根节点提取出来。
function listToTree(list) {
let temp_obj = list.reduce((map, node) => {
map[node.id] = node
node.children = []
return map
}, {})
return list.filter((node) => {
temp_obj[node.parentId] && temp_obj[node.parentId].children.push(node)
return !node.parentId
})
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
- 树结构转列表结构
function treeToList(tree) {
let node = null
let result = tree.map((node) => {
node.level = 1
})
for (let i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
if (!result[i].children) continue
let list = result[i].children.map((item) => {
item.level = result[i].level + 1
return item
})
result.splice(i + 1, 0, ...list)
}
return result
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 树结构查找
- 查找节点 思路:遍历到满足条件的节点则返回,遍历完成未找到则返回 null
function treeFind(tree, func) {
for (const item of tree) {
if (func(item)) return func(item)
if (item.children) {
const res = treeFind(item.children, func)
if (res) return res
}
}
return null
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
- 查找节点路径
function treeFindPath(tree, func, path = []) {
if (!tree) return []
for (const item of tree) {
debugger
path.push(item.id)
if (func(item)) return path
if (item.children) {
const findChildPath = treeFindPath(item.children, func, path)
if (findChildPath.length > 0) return findChildPath
}
path.pop()
}
return []
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14